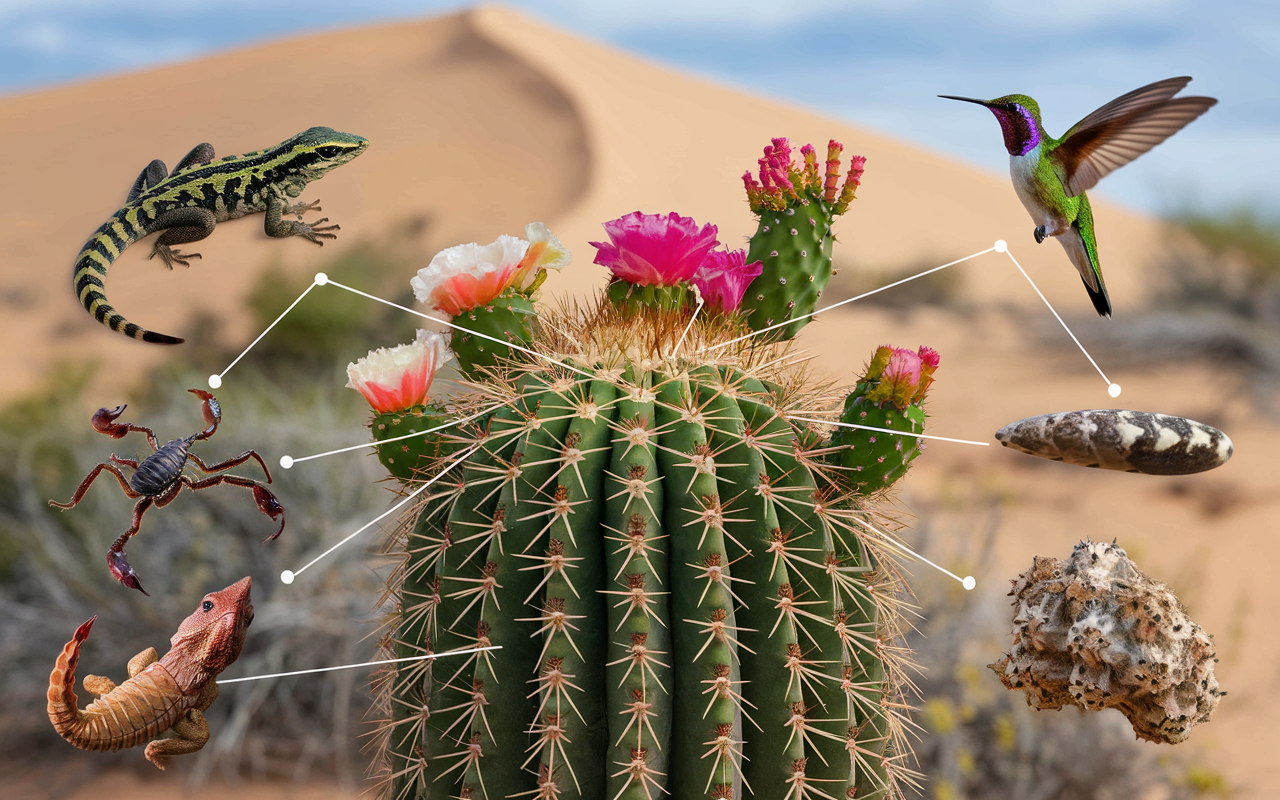
The food web for the desert is an intricate system that showcases the remarkable resilience of life. Despite the challenging conditions of deserts-with limited water, extreme temperatures, and scarce food sources-many desert organisms have found ingenious ways to survive and even flourish within this arid ecosystem. The desert food webs are complex, with every plant and animal depending on each other for survival. This article explores the awe-inspiring ways creatures in deserts manage to live in such a harsh desert environment.
The Importance of a Food Web in Desert Ecosystems
A desert food web is a beautiful tapestry of life, comprising multiple chains that intricately link plants and animals at different trophic levels. Each organism, from the primary consumers that eat desert vegetation to the secondary consumers and tertiary consumers that prey on others, plays a crucial role. This web of life ensures that all life forms in the desert biome can survive, highlighting the profound interconnectedness of the desert ecosystem.
Food Chains in the Desert
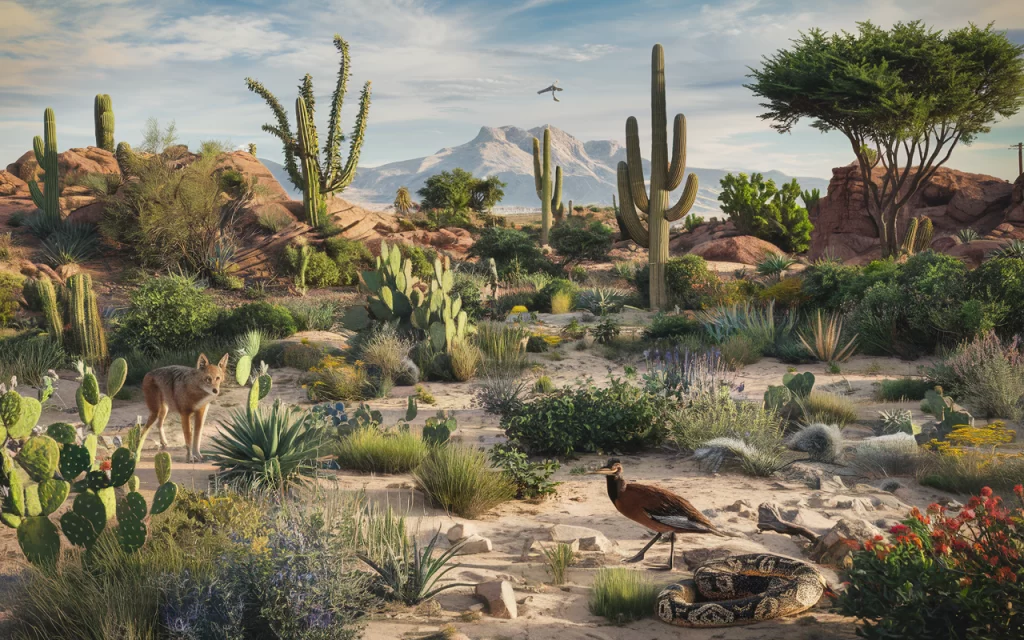

In every desert food chain, energy flows from plants to animals. The plants are the base, capturing energy from the sun and providing nutrition for herbivores. These herbivores are then consumed by secondary consumers, creating a cycle of life that supports the entire ecosystem. The balance of this food pyramid is vital, as each level relies on the one below it for sustenance.
Desert Vegetation: The Foundation of the Food Web
In deserts, plants are the first step in the food chain. These plants must be resilient to survive the arid landscape and dry climate. Desert vegetation such as succulents, cacti, and desert shrubs are typical, each adapted to conserve water in the rocky terrain.
Types of Desert Vegetation
Cacti and succulents store water in their thick leaves, while desert shrubs often have deep roots to reach underground moisture. These challenging desert vegetation types are essential for desert herbivores, providing vital nutrients in an otherwise barren environment.
Primary Consumers: The Plant Eaters
The primary consumers in the desert are the herbivores that eat the desert plants. These desert animals depend on the vegetation to gain essential nutrients for survival. Without these primary consumers, the food web would collapse.
Common Desert Herbivores
Some common desert herbivores include desert rodents, insects, and larger mammals like jackrabbits. Desert rodents, such as kangaroo rats, play a significant role in the desert food web. They feed on seeds and plants, while insects consume organic matter like dead leaves. With their specialized diets, these creatures allow the desert food web to flourish.
Secondary Consumers: Hunters of the Desert
The secondary consumers in the desert are the predators that hunt the primary consumers. Desert predators include snakes, hawks, and coyotes. These secondary desert consumers help regulate the population of herbivores, ensuring that plant life remains abundant enough to support the ecosystem.
Also Read: Jades Chinese Food: A Resturent The Best Asian Fusion Secrets
Adaptations of Desert Predators
Desert predators have particular adaptations that allow them to survive in the arid environment. Many are nocturnal, hunting at night to avoid the day’s extreme heat. For example, coyotes can go for long periods without water, relying on the moisture they get from their prey.
Scavengers: The Clean-Up Crew of the Desert
Scavengers like vultures and certain insects are crucial in keeping the desert environment clean. They feed on dead animals, recycling organic matter back into the soil. This process ensures that nothing is wasted in the arid ecosystem and helps prevent the spread of diseases that could harm other organisms in the food web.
How Scavengers Help Maintain the Food Web

Scavengers help break down dead organisms, returning nutrients to the soil. Without scavengers, dead animals would litter the desert environment, disrupting the food chains and leading to disease buildup. Scavengers are an essential part of the entire food web.
The Mojave Desert: A Unique Ecosystem
The Mojave Desert is a fascinating example of a desert ecosystem. Its wide variety of desert plants and animals have adapted to the harsh conditions. Although the Mojave Desert averages some of the hottest temperatures in North America, its desert organisms continue to thrive.
The Mojave Desert Food Web
The Mojave Desert food web includes desert animals like lizards, rabbits, and shrubs, such as creosotes. These organisms rely on one another for survival, with herbivores eating desert plants and secondary consumers like snakes and foxes preying on the herbivores. The Mojave desert food web shows how, even in such a dry and hot place, life finds a way to persist.
Surviving the Harsh Desert Environment

Desert creatures have developed unique adaptations to survive the harsh desert environment. From finding food in an arid wasteland to conserving water, every plant and animal must be resilient.
Specialized Diets in the Desert
Animals in the desert have specialized diets to help them survive the scarcity of food sources. Many desert creatures can survive on very little food, while others have developed methods to extract maximum nutrition from limited resources. For example, some birds and reptiles can eat tough plants and seeds that other animals avoid.
Threats to Desert Ecosystems
Desert ecosystems face many threats, particularly from human activity. The construction of the American desert highway system, urban development, and climate change are stressing these fragile environments.
Impact of Human Activity on Desert Food Webs
Roads and highways fragment habitats, making it difficult for animals to find food sources. Human encroachment also destroys desert vegetation and disrupts the desert food chains. As a result, many desert animals are losing their homes and food resources.
Closing Thoughts
The desert food web is a delicate balance of life, a testament to the power of nature’s adaptability. Every plant and animal, from the smallest insect to the largest predator, plays a vital role.
The food web for the desert not only helps us appreciate the complexity of the desert ecosystem but also underscores the urgent need to protect these unique environments from human-induced threats. It’s our responsibility to ensure the survival of these resilient organisms and the stability of their ecosystems.
Ultimately, the desert food web demonstrates how life can thrive even in the most challenging conditions. Each species, from plants to predators, works together to maintain a stable and functioning ecosystem.
FAQs:
A food web in the desert is a complex network of interactions between predators, prey, and plants, showcasing how energy flows through the ecosystem in arid environments.
Desert plants, like cacti and shrubs, are primary producers, converting sunlight into energy, which supports herbivores and, in turn, predators.
Key predators include desert foxes, hawks, and snakes. These animals control herbivore populations, maintaining balance within the ecosystem.



